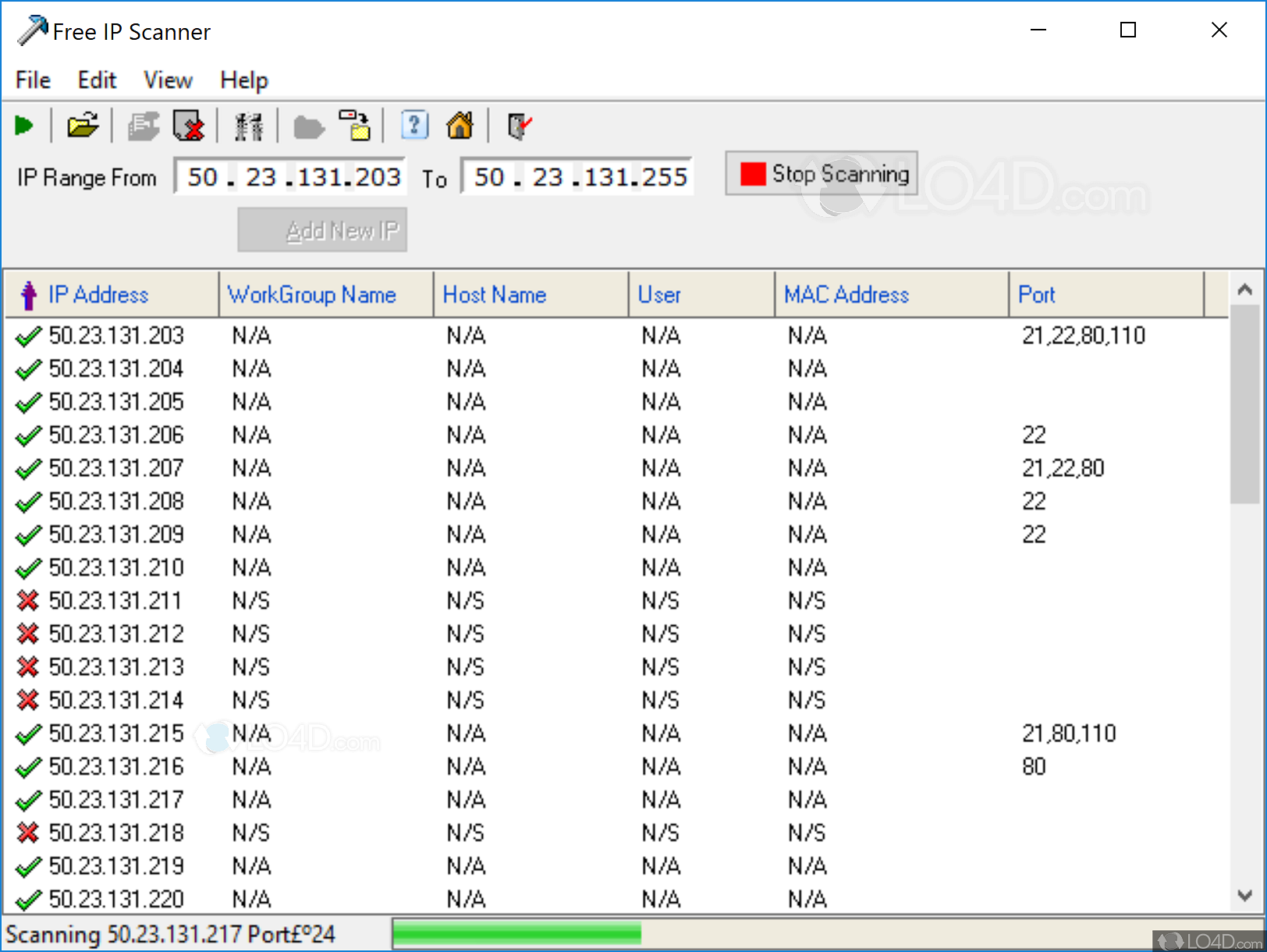
- Sep 13, 2020 Download XenArmor MAC IP Scanner Pro for Windows to find MAC and IP address of all systems in your network. XenArmor MAC IP Scanner Pro has had 1 update within the past 6 months.
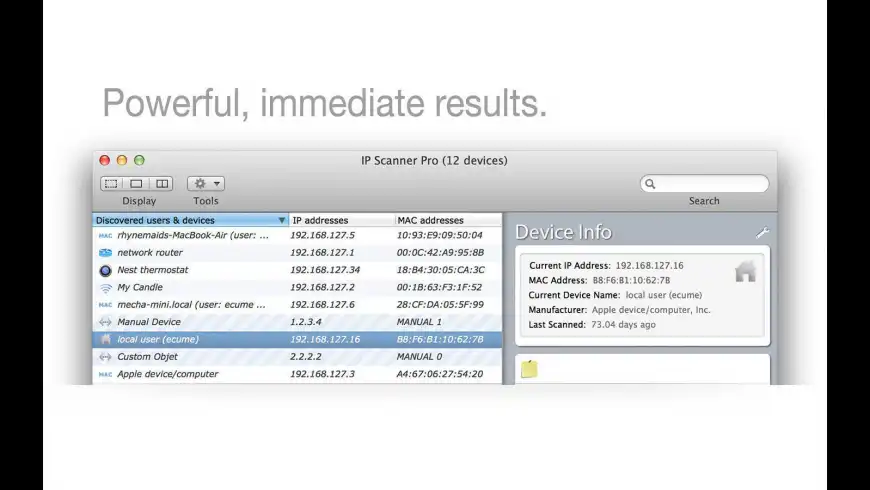
- IP Scanner Pro for Macintosh scans your local area network to determine the identity of all machines and internet devices on the LAN. Powerful results, yet easy and intuitive to use. IP Scanner is all about customizing the way you view your network. You may apply custom names and icons to the dev.
- Trusted Mac download IP Scanner Pro 4.02. Virus-free and 100% clean download. Get IP Scanner Pro alternative downloads.
- Ip Scanner Pro Mac Free Downloads
- Angry Ip Scanner For Mac
- Ip Scanner Pro Mac Free Online
- Ip Scanner For Windows 10
IP Scanner Pro for Macintosh scans your local area network to determine the identity of all machines and internet devices on the LAN. Powerful results, yet easy and intuitive to use. IP Scanner is all about customizing the way you view your network. You may apply custom names and icons to the dev.
Network scanning is a necessary task, but it can start off simple and rapidly become more complicated as your business gets larger. Manually finding IP addresses on your network is possible, but why do it yourself when there are so many tools to help you? Not only can network scanning tools help you find IP addresses, but they can also provide extra information for monitoring, troubleshooting, and keeping your network running efficiently.
My top choice for a network scanning tool is SolarWinds® IP Address Manager, as it works in an intuitive and easy-to-use way while offering a broad suite of tools and functions. It’s more approachable than some of the other tools out there and has a flatter learning curve for figuring out how to get started.
How to Find IP Addresses of Devices on My Network
Curious how to find IP addresses on-network? You may need to know about either static or dynamic IP addresses. If you can access your router, you may be able to simply view the client lists and get information like hostname and MAC address. Or you can use a device connected to the network to ping the network and view the ARP tables. Done manually in this way, you have to do everything through the command line. Use the prompt “ipconfig” on Windows to get network settings, followed by “arp -a” to view IPs plus MAC addresses.
However, this method doesn’t work across subnets. This means that if you have multiple subnets on your network, you have to go through each individual router or subnet to determine the IP addresses within the subnet. It becomes pretty clear as your network scales, manually scanning for IP addresses becomes an extremely complex task. Multiple subnets and an ever-changing string of devices connecting to and disconnecting from the network becomes problematic.
Instead of attempting to manually manage these aspects of your network, I recommend using an IP address manager (IPAM). These tools help you manage your IP addresses and troubleshoot problems, and they also help you find all the IP addresses of the devices on your network and determine the status of each one (dynamic, static, available, reserved, etc.). Some tools will also integrate with DNS and DHCP, and all of them will usually present data in a visual, interactive format. Many also allow you to save your network scanning results and present them in spreadsheets or reports.
Best Network Scanner Tools for 2021
SolarWinds IP Address Manager

This is my top choice for network scanning software.SolarWinds IP Address Manager (IPAM) with its IP Address Scanner feature is great for both beginner users and small businesses, and expert network administrators and large enterprises. With automated IP address tracking and integrated DHCP and DNS management, you can quite easily monitor your IP addresses and associated network information.
Ip Scanner Pro Mac Free Downloads
You can also see all your subnets and how they are structured, and which subnets and scopes don’t have much free space remaining. It allows you to flag capacity issues before they become a problem, so IP address issues don’t affect performance. I’ve also found it’s easy to find unused IPs and reclaim them to tidy up my networks.
This IPAM uses a clean and simple interface, without a steep learning curve like some other IP address managers. You can easily assign management or control permissions to other admins or admin groups, allowing you to simply delegate tasks within IPAM rather than needing to use another tool. The console is centralized, allowing you to see all the relevant information in one place, reducing the potential for error.
I consider SolarWinds IPAM to be a complete solution, and it’s my choice for an all-round lightweight tool you can use to scan and maintain your network. There’s a free trial available, so you can try it out, then level up to gain access to more features and greater scalability.
MyLanViewer
This is another strong business-level contender for network scanner tools. MyLanViewer is an IP and network scanner, as well as a traceroute tool and network monitor. It uses a buddy-list style window to display all your network computers, including important technical information about each one. It can scan your network to monitor IPs and let you know when any details change.
It also supports remote shutdown and other remote functions for each network computer. It can monitor hidden devices on your subnets and discover bottlenecks in your connection with its traceroute tool. I’d say this is a fine choice for business use—it has an easy-to-use interface and is suitable for beginners and advanced users.
SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper (NTM)
Looking for a combination network scanning and mapping tool? Network Topology Mapper is designed to use a unique, multi-layer discovery method using SNMP v1-v3, ICMP, WMI, CDP, VMware, Hyper-V, and more to create network diagrams with integrated OSI layer 2 and 3 topology data.
After performing auto-discovery to identify your WAN or LAN, NTM can build many useful network maps without having to rescan, which can help save valuable resources, bandwidth, and your time. You can also customize the size and placement of icons and surrounding text on network maps, so you can build the best topology view to suit your needs.
With the ability to schedule network scans, NTM can automatically detect network topology changes and inform you of new devices or changes. NTM can also help you more easily stay on top of network information and, since it’s FIPS 140-2 compliant, can support your ability to demonstrate compliance with PCI and other regulations requiring the maintenance of an up-to-date network diagram.
You can try NTM by downloading a 14-day free trial.
Angry IP Scanner
Looking for one of the best free tools? This is an open-source and free network scanning tool, with the ability to scan ports and IP addresses quickly and efficiently. The tool provides a report of data on each device on the network, including NetBIOS, MAC and IP address, computer name, and hostname. However, open-source tools often require more know-how on the user’s part and aren’t my usual pick for business use.
Angry IP Scanner can also produce reports in XML, CSV, and TXT format, which is useful for exporting data and other information within your business. It uses a multi-threaded scanning approach, which uses a separate scanning thread for each IP address. This helps to improve the scanning process and make it more accurate.
Angry Ip Scanner For Mac
Picking the Best IP Scanner
When I want to discover IP addresses on my network or scan for data generally, I tend to lean toward using a network scanning tool rather than trying to do it manually. Many network scanners have simple interfaces, and some go above and beyond in terms of ease-of-use and clean interface appearance. I like using SolarWinds IP Address Manager, as it contains a pretty hefty solution in a lightweight package, with a free trial for people who want to try it out without commitment.
Ip Scanner Pro Mac Free Online
Recommended Reading
Ip Scanner For Windows 10
Ultimate Guide to Network Monitoring: If you’re looking for more in-depth information on how to monitor and look after your network, take a look here for a beginner’s guide followed by more expert-level instructions.